THROMBOANGIITIS OBLITERANS [TAO]
Also called BUERGER’S DISEASE
Seen in young and middle aged males
M/c in smokers and tobacco users
M/c in lower limbs
Def:
Nonatherosclerotic inflammatory disorder involving medium sized and distal vessels with cell mediated sensitivity to type 1 and 2 collagen.
PATHOGENESIS
Immune reaction against collagen type ½ vessel wall
Smoking ie CO and nicotinic acid causes initial vasospasm and hyperplasia of intima
Thrombosis and obliteration of the vessel PANARTERITIS
Tunica media of the vessel exposed and is thrombogenic
Blood flow in inflamed vessels are turbulent causes injury to tunica intima
Veins and nerves are also inflamed
Ischemia of limb
CLINICAL FEATURES
Common in smokers b/w 20-40 years SMOKER’S DISEASE
Less blood flow to lower limbs intermittent claudication in foot and calf progresses to rest pain, ulceration and gangrene
Recurrent migratory superficial thrombophlebitis
Absence or feeble pulse in lower limbs
Exercise intolerance
May present as Raynaud’s phenomenon
INVG
Hb%
Arterial Doppler and Duplex scan
Transfemoral retrograde angiogram
Transbrachial angiogram
USG abdomen– abdominal aorta for block
TREATMENT
Stop smoking
Medical management*
low dose aspirin, clopidogrel, atorvastatin, cilostazole PDE inhibitor which improves circulation
Chemical sympathectomy– sympathetic chain is blocked to achieve vasodilation using xylocaine 1%
Sx*
Omentoplasty to revascularize the affected limb
Lumbar sympathectomy– increase cutaneous perfusion and promote ulcer healing
Gene therapy*
Intravascular injection of vascular endothelial growth factor– promotes angiogenesis
RAYNAUD’S PHENOMENON
An episodic arteriolar spasm
Coffman criteria:
Episodic attacks of well demarcated reversible self-limiting color changes on exposure to cold/ emotional stimuli which are bilateral and last for 2 years
Etiology
Occurs in upper limb with normal peripheral pulses
Abnormal sensitivity to cold upper limb arteriolar spasm blanching, cyanosis and later flushing
If spam persist results in GANGRENE
Symp precipitated and observed by placing hands in cold water
Working with vibrating tools like road drills, chain saws etc
Often a/w CREST syndr
Collagen vascular diseases– scleroderma, rheumatoid dis
CREST Syndrome
Calcinosiscutis
Raynaud’s phenomenon
Esophageal defects
Sclerodactyly
Telangiectasia
Clinical features
Commonly bilateral
Common in young females
Medial four digits and palm involved– Thumb spared
Blanching/ syncope/ pallor
Dusky cyanosis– asphyxia
Rubor/ painful red engorgement– sign of recovery
Gangrene or ischaemic ulcer along the tips of the finger– vasospasm longer
Peripheral pulses normally felt
Types
Primary Raynaud’s phenomenon:
Due to increased sensitivity of alpha 2 receptors to norepinephrine
Decreased nitric oxide and endothelin 1 in endothelial cells
Increased serotonin and thromboxane
Common in females
b/l involving all digits
Secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon:
Vasospasm due to underlying cause like collagen vascular disease, SLE etc
Positive for autoantibodies
Equal in both sexes
Invg
DSA/MR angiogram
Arterial Doppler
Duplex scan
ANA– Antinuclear Antibody Assay
Treatment
Treat the underlying cause
Avoid precipitating factors– protect from cold/ proper dress/ hand warmer/ gloves
Vasodilator/ low dose aspirin
ACE inhibitors, Calcium channel blockers
Cervical sympathectomy – for non healing digital ulceration
SUBCLAVIAN STEAL SYNDROME
Obstruction of first part of the subclavian artery vertebral artery provides collateral circulation to the arm by reversing its blood flow
Causes CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA WITH SYNCOPAL ATTACKS, visual disturbances and diminished blood pressure in affected limb
More common on left side.
Clinical Features
Vertebrobasilar symptoms like dizziness, syncope, visual disturbances, vertigo
Pain, heaviness, paraesthesia and fatigue in the arm– aggravated by exercise
Radial pulse on both side asymmetrical
BP on affected side is 20mmHg low compared to normal side
Invg
Duplex scan
Angiogram
DSA
Treatment
Transluminal balloon angioplasty
Endartrectomy or bypass graft common carotid- subclavian graft
EMBOLISM
EMBOLI means a PEG
Solid, liquid or gaseous material which is floating and travelling in blood stream, eventually blocking the blood vessel on its pathway
M/c site– Lower limbs [75%] bifurcation of common femoral artery
Types
Arterial emboli:
Cardiac source– mural thrombus
Non cardiac– aneurysm, atheromatous plaque in proximal artery
Idiopathoic
Venous emboli– DVT causing pulmonary embolism
Fat emboli
Air emboli
Venous –arterial paradoxical emboli– intracardiac shunt [ASD] or intrapulmonary shunts [ AV malformations]
Clinical Features
Sudden, rapid development of pain
Limb rapidly cold and mottled with blebs
Loss of sensation and movements
Absent of distal pulse
Collapsed veins, cold limb distal to level of block
Edema and presence of blebs distally
INVG
Doppler angiogram gold std
ECG and echocardiography
PT, APTT, INR, BT, CT
Once embolism occurs , irreversible changes occur distally in 6 hrs
Hence ideal period of intervention is within 6 hrs
Treatment
Immediate infusion of 5000-10000 units of IV heparin
Sx Embolectomy– TOC
Endvascular therapy
Intrarterial thrombolysis using Urokinase
Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy
Drugs like streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator like alteplase, reteplase etc
C/I for Thrombolysis
Recent stroke
Recent major Sx or major bleed like varices
Recent eye Sx
Active duodenal/ gastric ulcer
Pregnancy
Uncontrolled HTN or coagulation disorder
Saddle Embolus
Embolus blocking at bifurcation of Aorta
Etiology
Mural thrombus after MI
Mitral stenosis with A fib
Aortic aneurysm
Clinical Features
Claudication pain in the buttocks
Rapidly progressive ischemia features in lower limbs
Gangrene
Associated infection
Invg
Arterial doppler
Aortic angiogram
USG abd
Treatment
Inj heparin 10,000 units
Embolectomy
Open arteriotomy
Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infection
Caisson’s Disease
Also called decompression disease
Due to rapid decompression from high altitude, aircraft, compressed air chambers, deep sea divers
Bubbling of nitrogen blocks the small vessels
C/F
Joints and muscle pain
Spinal cord ischemia causing neurological deficits
Chocking with chest pain, tightness and dry cough if lung affected
Treatment
Oxygen therapy
Recompression and gradual decompression in special chamber
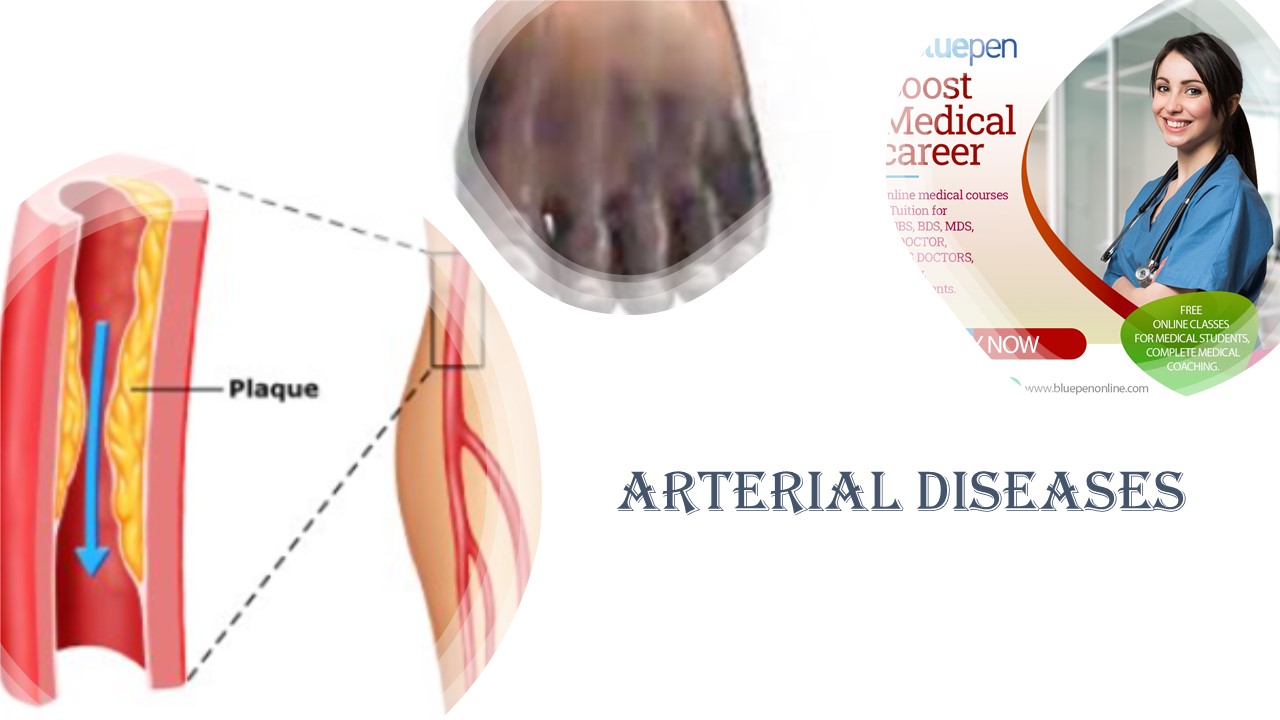
ANEURYSM
DEFN:
Abnormal permanent dilatation of localised segment of arterial system
Diameter 50% more than expected
Atherosclerosis m/c cause
Due to destruction and loss of stability of tunica media
Classification
True aneurysm:
Contains all the three layers of artery
False aneurysm:
Contains single layer of fibrous tissue as wall of the sac
Usually occurs after trauma
Types
Fusiform-- uniform dilatation of entire circumference of arterial wall
Saccular– dilatation of part of circumference of the arterial wall
Dissecting– tear in the intima blood dissects between inner and outer part of tunica media of the artery
Causes
Acquired:
Degenerative– atherosclerosis– M/c, mucoid degeneration of intima and media
Traumatic
Infective– syphilis, mycotic, TB, arteritis and a/c sepsis
Collagen diseases like marfan’s syndrome, polyarteritis nodosa, Ehler Danos syndrome
Congenital:
Berry aneurysm
Congenital Av fistula
Sites
Aorta– M/c site
Femoral artery
Popliteal A
Subclavian A
Cerebral, mesenteric, renal and splenic arteries
BERRY ANEURYSM:
Multiple aneurysms occurring in circle of willis
Clinical Features
Swelling at the site– pulsatile, smooth, soft, warm, compressible, with thrill on palpation and bruit on auscultation
Distal edema– venous compression
Altered sensation– compression of nerves
Erosion into bones, trachea or esophagus
Invg
Angiogram- IOC
DSA
Doppler study
Treatment
Reconstruction of artery using arterial graft
Arterial endoaneurysmorrhaphy
Therapeutic embolization
Clipping of vessels
Complications
Thrombosis and distal ischemia
Emboli causing acute arterial obstruction
Pressure effects on bones, skin, oesophagus, nerves, stomach
Rupture
Infection of aneurysm
DISSECTING ANEURYSM
Mainly an AORTIC DISSECTION
No aneurysm
Dissection of media of AORTA after splitting through the intima creating a channel in the media of the vessel wall
Causes
Hypertension– M/c association
Cystic medial necrosis
Marfan’s Syndrome and collagen diseases
Trauma
Weakening of elastic layers of the media due to shear force
Clinical features
M/c in ascending aorta [70%]
Can occur in ascending arch or thoracic descending aorta
Dissected aortic channel gets lined by endothelium– reopens distally into the aorta causing double barrelled aorta
Associated with aortic insufficiency
Atherosclerosis not usual cause
Classification
Debakey’s classification:
Type 1: Dissection begins in ascending aorta extends into descending thoracic aorta– 70%
Type 2: Dissection originates in ascending aorta and extends only upto the origin of the major vessel– safe type and less complication
Type 3: Begins in the descending thoracic aorta beyond the origin of the left subclavian artery
Stanford classification:
Proximal– includes DeBakey’s type 1 and 2
Distal– include DeBakey’s type 3
Clinical Features
Pain in the chest and back– excruciating
Ischaemic features due to blockage of different vessels
Invg
CXR– mediastinal widening
Arterial Doppler
Angiogram
Treatment
Antihypertensives
Surgery - Using Dacron graft, reconstruction of the aorta.
VASCULAR LESIONS
HEMANGIOMA
M/c tumour in children
Benign vascular endothelial tumour
Common in girls
Shows cellular endothelial hyperplasia with increased mast cells
Site: skin and subcutaneous tissue, also in liver, brain,lungs
Grows rapidly in first year and 70% cases later involutes after 7 yrs
Early proliferation lesion bright red in colour
Large haemangiomas associated with visceral anomalies
Types:
Capillary– Strawberry hemangioma
Cavernous hemangioma
Complications:
Platelet trapping and severe thrombocytopenia– life threatening
Ulceration
Bleeding
Airway block
Visual disturbances
Capillary vascular Malformations
Salmon Patch
Port Wine Stain
Salmon Patch
Also called Nevus Simplex
Common in 40% newborns
Presents at birth
Site– common in nape of neck, face scalp and limbs
Involves wide area of skin
Regresses spontaneously and completely
Port wine Stain
Present at birth and persist throughout life
Persist as smooth, flat, reddish blue/ intensely purple area
Site– head, neck and face
Often with maxillary and mandibular dermatomes of 5th Cranial nerve
Surface later becomes nodular and keratotic
Often associated with sturge weber syndrome, klippel trenaunay weber syndrome
Treatment:
Laser, excision and grafting
CAVERNOUS HEMANGIOMA
Present at birth
Consist of multiple venous channels
Size increases gradually
Contains feeding vessels
Sites: Head, neck, face, limbs, tongue and liver
Large or multiple ones can cause congestive heart failure due to shunting of large quantity of blood
Cavernous hemangioma of liver is the m/c benign tumour of the liver
Clinical Features
Compressibility and bluish surface
Nontender unless infected
No transillumination
Invg
Usg
Doppler
Angiogram to find feeding vessels
MRI/MR angiogram
Complication
Haemorrhage
DIC
Thrombosis
Infection, ulceration and septicaemia
High output cardiac failure
Treatment
Sclerosant therapy– first line
Causes aseptic thrombosis and fibrosis of haemangioma
Ligation of feeding artery
Therapeutic embolization
Laser ablation– CO2/ Nd:YAG laser
BDS TUITION (Bachelor of Dental Surgery Coaching)
Coaching for 'Mbbs Students', 'Bds Students', 'Mds Students', 'Bams Students', 'Bpt Students', 'Bhms Students', 'Nursing Students', 'PreMed Students', 'Md Students', 'Doctor Students'
Connect with Bluepenonline
"Mbbs Tuition" "Bds Tuition" "Bams Tuition" "Next Tuition" "NeetPg Tuition" "Bpt Tuition" "PreMed Tuition" "Md Tuition"v"Medical Subjects Tuition" & "Medical Lecture Notes"
Please search in google or edge as follows to connect with Bluepenonline, Find Private & Affordable MBBS Tutoring, MBBS TUTORS, Online MBBS Tuitions, online classes for mbbs students, MBBS Tuition near me, BDS Tuition, Online BDS Tuitions, BDS Tuition near me, pre-med tuitions for international students, Online BAMS tuition, BAMS Coaching classes near me, BAMS coaching classes online, Online BAMS Coaching Classes, Next/NeetPg Coaching, ayurveda tuition, Ayurvedic medicine courses,..etc